Company Introduction
POWERSHOP
Powershop is an online power company that operates as an electricity retailer in Australia. Powershop was founded initially in New Zealand but later expands its business in Australia. Powershop claimed to be the cheapest electricity retailer for the common consumer in the main centers and later, its claim was declared right by the Ministry of Economic Development. (CHURCHOUSE, 2009)
The company declares to be the first electricity company in the world that allows consumers to make choices among different brands of electrical power programmed on the website and can change their brands/plans only with the click of a button. These brands of power differ on the product offerings based on sponsorships, lower prices, or environmental benefits. Consumers can either allow the system to routinely buy power from the cheapest supplier available, or they can log in regularly to take benefit of special offers.
Powershop allows the customers to keep an eye on their electricity consumption and its related cost anywhere, anytime. The company’s toolkit facilitates the consumers to control their power usage and also offers discounts regularly allowing consumers to save their money. Powershop will read the electricity meter once a month, but users are expected to read the meter themselves more frequently to identify their power usage more. The consumption pattern of power is presented to the customers in the form of charts and graphs that provides the usage figures of every hour. (Parkinson, 2014)
Besides, the consumers can purchase electric power for one day or a week or even for a year ahead to avoid the hassle of bill surprises and payments. This toolkit could be operated through a computer or any electronic gadget, for instance, mobile or tablet. The power is sold under different brands known as “Powerpacks” offered by the company are:
- Special Packs: that offers power at low prices to save consumers money from time to time.
- Future Packs: allows the consumers to purchase electricity for upcoming months. The pack allows the stocking up before summer and distributing the costs over the year ahead.
- GreenPower Packs: allows the consumers to play their role in environmental impact.
- Top-up Packs: These are the instantly available power packs that are available all the time and can be consumed promptly.
All the purchase transactions are carried out through the company’s website, while the payment is made through debit cards, credit cards, or online banking. Customer support is provided through different communication mediums, like, telephone, Skype, and social media sites.
PowershopMarket Analysis 2022
In 2012, Australia was ranked as the 8th largest producer of energy in the world. The production of energy is an emerging segment, with the energy production growing at an average rate of 2% yearly over the last 10 years. Australia has very diverse energy resources such as coal (black and brown), oil, uranium, natural gas, and renewable energy sources.
As the energy demand is escalating and the country is facing a limited amount of non-renewable sources, renewable energy is getting more attention and is attracting numerous existing and new companies to come up with renewable sources. The electricity supply segment of the industry accounts for 27% of Australia’s total energy consumption during the years 2013 to 2014. While, renewable input to Australian electricity generation raised to approximately 15% during the years 2013 to 2014, up from 8% in 2003–2004. The biggest source of renewable generation is Hydro, while wind and solar continue their struggle to gain their shares. Wind generation increases by 29% in 2013–2014, whereas solar generation by 27%. Altogether these fuels accounted for 4% and 2% respectively of entire electricity generation in Australia.
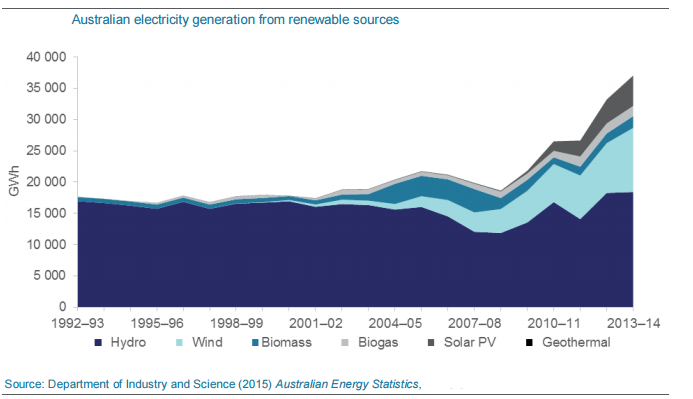
SOUTHEAST QUEENSLAND MARKET
The electricity retail segment of the energy industry in Australia is becoming more vibrant as more competition persists to evolve and are offering new sort of retail offers, energy services, and technologies giving customers better choice and control over managing and utilizing the electricity. In Queensland, there are two electricity distribution zones:
- Energex covers South East Queensland
- Ergon Energy covers the rest of the state.
The costs of energy supply to customers in southeast Queensland serviced by Energex are comparatively lower than those in Ergon Energy’s region. This is mainly because in the Ergon region the transportation costs are higher because of the long distances and fewer customers to share the costs of energy infrastructure. Households in the Energex zone have the option to choose from a variety of market and electricity offers offered by more than eight retailers in the region. Annual electricity bills for these offers ranged from $1320 to $1552.
Competition
The competition in the retail electricity markets of South East Queensland continues to be very effective. Many industry drivers, including, changing cost of inputs, fluctuation in demand levels, technologies change, innovation, new entrants, and change in customer preferences are giving birth to the development of effectively competitive markets. In this industry, competition is extremely price-based as there is less differentiation between the products and services offered by different companies.
Being an innovative and online electricity retailer, Powershop faces direct competition from the other innovative and online energy retailers in the market. Hence, the direct competitors of Powershop are:
Click Energy
Click Energy, is an Australian energy retailer selling electricity to private and business customers in New South Wales, Queensland, and Victoria. The company was founded in April 2006, and by June 2006 it was able to acquire its electricity license. Click Energy started its operations in Victoria initially but in March 2007, the company entered the Queensland electricity market and in March 2013 enters the New South Wales electricity market. The company is distinctive in being a devoted online energy retailer. Click Energy has positioned itself in the market as the “Iconic of power companies”. Click energy offer discounts to daily supply charges and unlike a lot of utilities, it doesn’t charge any credit card surcharges, nor it sends snail-mail bills. It has also found an innovative way of smoothing out the increasingly painful cost of electricity, by borrowing the model of a mobile phone contract and adapting it for the electricity market. (TUTTY, 2013)
Click charge its users a set direct debit amount every month, and once it has read a meter quarterly, the user will get a bill or a credit, depending on whether he has exceeded or undershot the monthly charges already paid.
power
Opower is a publicly held service company that offers cloud-based software to the utility industry and its customers. The company works with more than 95 utilities and serves more than 50 million homes in 9 countries. Opower’s software gives customers better information about their energy usage, together with customized means to save money and energy. Its apps include games where users can compete with their friends or neighbors to observe who is the most energy-efficient, and Wifi thermostats that allow the users to turn their heating and cooling systems up or down from their Smartphone to decrease the utility’s baseload requirement.
Opower’s technology platform evaluates over 300 billion meter reads to deliver its services and has created sufficient energy savings through behavior change to power all the homes in a city of 1 million people for a year. The average customer getting the Opower platform has cut energy consumption by over 2.5%.
In 2012, Opower did a great deal to produce Energy Australia’s “eWise” platform, promoted on Channel Nine’s The Block. In 2013, CNBC News in the US-listed Opower in its “Top-50 Disruptors” list. (Gibson, 2013)
Sungevity
Sungevity is a solar electricity company founded in 2007 in California by former Greenpeace activist turned entrepreneur Danny Kennedy and is operating in Australia as well. It was the first in the US to offer quotes within 24 hours by using aerial satellite imagery to work out a home’s solar potential, removing the need to send a representative round to a place to measure the roof up. The company also offers “pay-as-you-go” solar plans that allow a person to get cheaper power and free solar panels at the same time.
The company operates by leasing the panels to customers who pay them back over time. Another option it offers to its customers is that the company installs panels for free on their roof and charges them a competitive set price for the power they generate over a 20-year contract. The company charges a tariff fee somewhat less than the standard rate in the region. Presently, Australia has over 1 million solar rooftops after swift growth in the past five years and companies like Sungevity seem to be ready to carry on the trend.
Besides these online retailers, many advanced startups are taking place in the market like BioSystems, Aquagen, and Ocean Power Technologies that are entering the market with innovative technologies.
Although Powershop is facing intense competition from the above-mentioned competitors and the electricity giant suppliers, yet Powershop has been able to attract a large number of growing customers over the 2 years Powershop can grow its customer base by almost one-third within a year (Vorrath, 2016) as shown in the graph below:
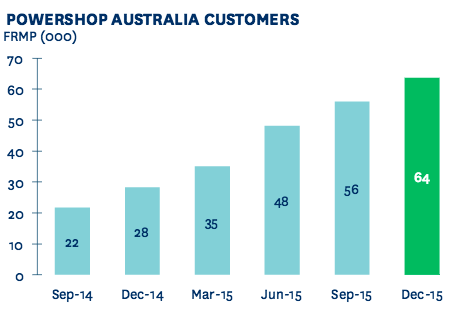
Powershop PEST ANALYSIS
PEST Analysis is a framework used to analyze the external macro-environment of an organization and stands for Political, Economic Socio-cultural, and Technological analysis. Analyzing these environmental factors helps the company to determine the market trends and the risks involved before launching a new product or expanding its operations in a new market so that the company could formulate its strategies accordingly. (Parnell, 2013)
Political
The political factor helps the company to analyze the rules, regulations, and legislation connected with the country in which the company plans to offer its products. This includes issues like tax guidelines, political stability, safety regulations, trade regulations, and employment laws. (Gupta, 2013).
Australia is one of the countries that contribute a lot of emissions to global warming and environmental degradation. Most of the CO2 emissions come from the energy sector- from electricity generation and energy export. The Australian government is working towards reducing pollutions via different legislation and policies. Most of them are aiming to promote renewable energy generation and substituting conventional energy sources with renewables.
The rules of the Australian Energy Market have been developed by the Australian Energy Market Commission (AEMC), and enforced by the Australian Energy Regulator (AER), which is a body of the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC). Energy industries in Australia, including the oil and gas industry, transport fuels, and the electricity industry are governed by policies with a principal focus on economic efficiency and development. The focus on economic efficiency has resulted in significant industry reforms since the early 1990s aimed primarily at opening up markets to competition in line with the National Competition Policy.
Goals of energy policy in the electricity market complementary to economic efficiency include energy security, safety and customer service, greenhouse gas emissions management, energy efficiency, and support for renewable.
Economics
Under this factor, Companies check up the economic concerns that are vital to have an impact on the company’s operations. This would include factors such as economic growth, the unemployment rate, interest rates, the business cycle, inflation, and policies pursued in the country (Peng & Nunes, 2007).
According to National Data, the energy industry accounts for 7% of the Australian gross value added. Therefore any changes and policies implemented on such a big part of the national economy must be carefully analyzed with emphasis on long-term effects.
In an economy heavily dependent on electricity, the industry’s core services are very well-established and used frequently. These trends protect electricity retailers from any large periods of decline, as electricity demand tends to remain fairly stable. However, the rising prevalence of solar panels and other energy-saving products has slightly reduced electricity demand over the past five years. (World, 2016)
As stable as the growth in the energy sector might be, there are still times when the total production unexpectedly increases or decreases. Most of these jumps can be explained by economic factors like supply and demand mechanisms or financial crises. There can be seen a visible peak in production in 2008, followed by a decrease in years 2009-2010. The sudden drop in production can be explained by the financial crisis in 2008 that the Australian economy has experienced in the years 2009-2010. Looking at the Gross Domestic Product percentage changes, there is a visible decrease in these years. A similar correlation between energy production and GDP can be seen also in the year 1999. (Ball, 2015)
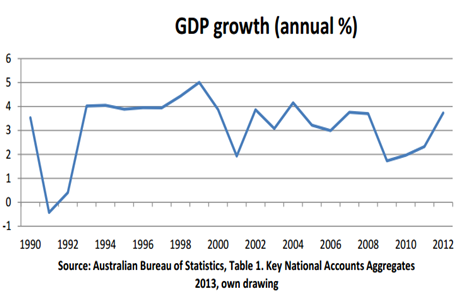
Social and Cultural Factors:
This factor deals with the socio-cultural environment of a country and includes lifestyle attitude, cultural limitations, education, and customer demographics (Gupta, 2013).
In Australia, people’s attention shifts from primary needs like employment, income, and consumption, to more elaborate needs for other goods like clean air and ecology. People are now more inclined to purchase those products and services that help in reducing environmental impact. Many consumers find the new technologies appealing but they are yet hesitant to adopt the new and emerging technologies because there are significant gaps in information about what these technologies mean for them. This may indicate a need to build customer confidence, knowledge, and understanding to improve customer outcomes. (AEMC, 2016)
Technological:
The new and advanced technologies and the services they provide are creating opportunities for retailers to develop products and offers that better align with customer preferences. The drivers of investment and development are increasingly being devolved to consumers as technological change allows consumers to choose how their energy is sourced and used. These technologies and services are also creating opportunities for new businesses that place competitive pressure on the “traditional” retailer business model. Presently, new businesses and “traditional” retailers are both competing to offer customers solar photovoltaic panels and electricity storage batteries individually and in combination with a variety of financing options, including an outright sale, lease, and power purchase agreements. Other products and services being offered to customers include home energy management systems and online energy usage information.
Powershop SWOT Analysis
SWOT is a great indicator of an agency’s strategic ineptitude. This involves creating a two by two grid and populating it with a list of incredibly obvious client strengths and weaknesses, and another list of equally palpable opportunities and threats (News: Marketing Magazine, 2005).
Strengths
Powershop’s corporate capabilities which also counts as the company’s strengths and competitive edge are:
- Powershop is New Zealand’s first online electricity retailer that is offering online energy services in Australia.
- Powershop is supported by its parent company, Meridian Energy.
- Through differentiated brand marketing and the use of different channels to reach customers (including Smartphone applications) Powershop was able to engage customers in their retail electricity purchase and in the process take significant market share. (FREAR, 2014)
- The company has been able to maintain a strong brand image in the eyes of its customers.
- The company has high visibility in local markets.
- Over the course of 5 years, Powershop has been able to maintain a list of loyal customers.
- The company also offers high-quality electricity from ethical sources, hence maintaining its corporate social responsibility strategy.
- Powershop has highly qualified and motivated staff
Weaknesses
- Limited geographic reach that is the company is operating in New Zealand and few regions of Australia.
- Lack of brand recognition in the international market.
- High expenses for expansion in international markets.
- Lack of in-house expertise to compete in the international market.
Threats:
- The decline in Electricity prices would lead to lower profits
- Presence of much larger companies like Energex who had been operating in the market as market leaders for decades.
- Consolidation of the power industry in Australia
- Intense competition from rivalry because of lack of differentiation as many competitors offer the same products.
- Technology is easily copied and could abruptly change which requires the company to continuously improve itself to sustain itself in the market.
- The economic recession
Opportunities:
- Potential to expand its renewable energy portfolio.
- Expanding its business internationally especially in emerging economies. The company could market its services globally increasing the sales of its products hence generating high revenues for the company.
- Increase brand awareness through advertising
- Can further expand its product by diversifying the product line
- As Powershop Services are environmentally friendly and therefore help in reducing pollution attracting more customers who are attracted towards environmentally safe products.
Consumer Behavior Analysis
In Australia, many customers are now shopping around for energy (electricity or gas) deals. 26% of residential and 30% of small business customers had been actively investigating options in the year 2016. However, the switching rate among small electricity customers remained steady at 16%.
New and emerging technologies and services are changing the way customers interact with energy and how customers interact with retailers, as shown in the figure below:
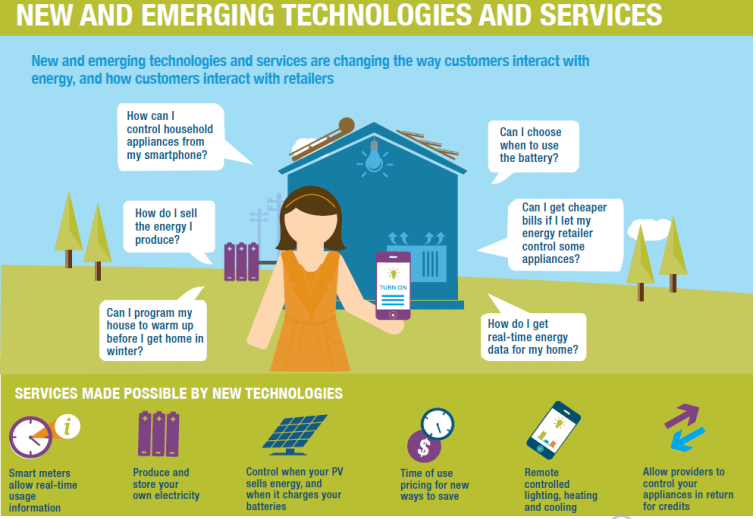
The majority of customers are satisfied with their current retailers in the electricity market and faces resistance to change when opting for a new retailer. This was proved by a survey carried by the Australian Energy Market Commission (AEMC) and found that 60% of residential customers were satisfied with the level of market choice, a substantial increase from 48% from the years 2014 to 2015. 70% were satisfied with their current retailer, an increase from 63% from the year 2014-2015, while 7% were dissatisfied. (AEMC, 2016)
Talking about South East Queensland, Queensland’s adoption of the NECF on 1 July 2015 means the AER’s Energy Made Easy website is now available in the market, yet only 1% of South East Queensland customers knew about the website. Hence, a lack of awareness exists in the market that could be promoted through marketing and advertising.
The demographic characteristics and attitudes across the spectrum of customers of electricity retailers are:
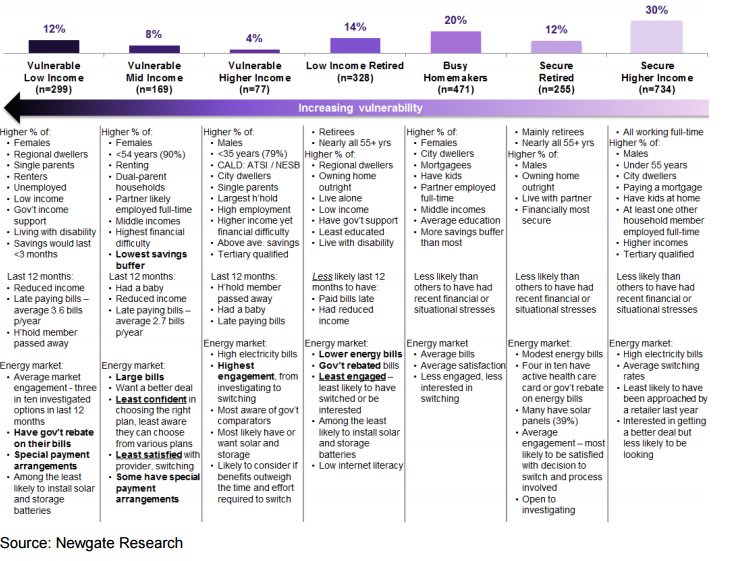
PowerShop Target Market:
The target market of Powershop comprises all market segments, people of all demographical living in South East Queensland. The below table specifies the target segments of Powershop:
| MARKET SEGMENTS | VARIABLES | CONCENTRATION |
| Demographic | Age | 10 years onward |
| Gender | Male, female, and teenagers | |
| Income | All income groups specifically Mid-income and Low income. | |
| Occupation | All occupations specifically, working-class, single parents, and retired people | |
| Religion | All religions | |
| Nationality | Australian and immigrants living in Australia | |
| Race | Respectable of race. | |
| Education | All educational levels, even for the uneducated. | |
| Geographic | Country | Australia |
| Region | South East Queensland | |
| Population Density | High | |
| Climate | Moderate, with an average of 7 hours of sunlight | |
| Psychographic | Social class | All social groups |
| Lifestyles | Urban, rural, and even remote areas | |
| Behavioral | Benefits | High-quality services, affordable price, user-friendly. |
| Loyalty status | High |
Consumer Behavior of the Target Market:
The majority of customers of online energy retailers are people belonging to the mid-income segment who tend to be dual-parent households that are renting and have only one parent working and a child living at home. They tend to have higher electricity bills and are more likely to miss or be late paying a bill. They do not clearly understand the links between energy use and costs and therefore are at greater financial risk if they are not on the right energy offer. They are even not aware of the plan they are on or that they can choose from various plans from their own or different retailers. Most people hesitate because they have limited understanding of the terminology used on bills, such as kWh, or the difference between standing and market offers; and will tend to stick with their existing retailer because they have a risk-averse nature, which is partly due to a lack of financial capacity, fear of making a wrong decision and concern about how their circumstances may be perceived by a retailer.
On the other hand, a large number of customers seemed to need a noticeable trigger event to overcome their inertia, like:
- Moving house or getting solar panels installed;
- Repeated poor customer service and not being able to reconcile issues;
- Direct approaches by retailers with an offer or incentive (such as pay on time discounts, no lock-in contract, etc);
- Reaching the end of a contract;
- Wanting to change their billing arrangements (ie., move to monthly bills);
- Word-of-mouth recommendations from family or friends; and
- Increased prices or (for the few who have solar) decreased solar feed-in tariffs.
Hence, besides Powershop could face resistance to change, yet there is a large portion of the market that is ready to accept the change but they still lack awareness and information.
This awareness and information could be provided to the intended customers through the following Marketing Mix Plan:
Powershop Marketing Mix
Product:
The company allows consumers to make choices among different brands of electrical power programmed on the website and can change their brands/plans only with the click of a button. Consumers can purchase electric power for one day or a week or even for a year ahead and could monitor their electricity usage and cost. The toolkit could be operated through a computer or any electronic gadget, for instance, mobile or tablet. The power is sold under different brands known as “Powerpacks” offered by the company are:
- Special Packs: that offers power at low prices to save consumers money from time to time.
- Future Packs: allows the consumers to purchase electricity for upcoming months. The pack allows the stocking up before summer and distributing the costs over the year ahead.
- GreenPower Packs: allows the consumers to play their role in environmental impact.
- Top-up Packs: These are the instantly available power packs that are available all the time and can be consumed promptly.
All these products are purchased through the company’s online website only.
Price:
The pricing of the new market will remain the same as it was in other existing regions. Yet, to grasp the market, Powershop has already been adopting the market penetration strategy through which the product is offered at lower prices comparatively from the competitors. This strategy will help the company to attract the target market which is more price-sensitive and will be willing to buy the product from that manufacturer that offers the minimum prices. The company is having 54% of the Mark up, while bundle pricing will be offered to customers who are going to purchase the energy for one or two years ahead.
Placement:
The company is operating through online mediums and will be operating through the internet on its website. A separate new page would be added to the website for the new region with an attractive layout and convincing messages. Later with further expansion, extended websites will be bought for separate regions.
Process:
Powershop will be operating as a retailer, hence distributing the electricity produced by the producers to the end-users.
![]()
The company will be making agreements with the production companies and will do all the merchandise, legal formalities, and marketing and in the end will provide the customers, their desire amount of energy according to their preferences. The process is shown in the below figure
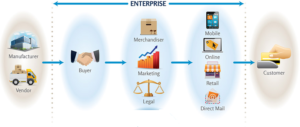
Promotion:
The company will be promoting itself in the new region aggressively by using both traditional and digital media. In traditional media, the promotion will be done through sponsorship, TV ads, and celebrity endorsement while in digital media the company’s product will be promoted through weekly promotional and competition activities on social media sites to attract and interact with customers on regular basis.
The company needs to create a brand image and brand recognition among its target market. But as the promotional budget of the company is limited, therefore, the company will be highly emphasizing low-cost promotional activities while ensuring reaching maximum audiences. For the promotional, the company adopted the following Media:
| Media | Percentage of budget | Budget in Dollars $ | Reach level | Duration |
| Broadcast media TV | 30% | $15000 | High and to the mass population | 1 month after operation in a new region |
| Internet/online ads | 40% | $20000 | High and Mass population | Monthly ads for the first year on famous websites |
| Print media | 10% | $5000 | Average and mass | Prints ads in the local newspaper. |
| Sales promotion | 10% | $5000 | High and focused | Sales promotion for each month |
| Broachers and Flyers | 10% | $5000 | High and focuses | Brochures and flyers will be placed in the targeted region. |
| Total | 100% | $50000 |
The company will be promoting the website through other internet communication channels like AdWords advertisement as “search Ads” package, social media sponsor ads like Facebook advertising with specific and filtered consumer profile.
Financial Feasibility:
The plan is financially feasible for the company as the estimated budget for the advertising would be effective enough to promote the company’s offerings efficiently and the company has the revenues for the distribution of energy in the new region to increase its existing sales.
Implementation Plan
| steps | Activity | Date | Rationale |
| 1. | The hiring of the marketing manager and marketing team for the new region. | By 30th December 2016 | To implement and carry out all activities of the marketing plan. |
| 2. | Clearly defining the target market | By 15th March 2017 | To understand the customer’s needs and wants |
| 3. | Designing and implementing the product strategy | By 30th March 2017 | To design the product according to the customer’s needs. |
| 4. | Implementing pricing strategy | By 30th March 2017 | Pricing each product to make the products ready. |
| 5. | Implement the placement strategy by | By 30th April 2017 | Making the product available in the market. |
| 6. | Implementing the promotional strategy | By 30th April 2017 | Creating brand awareness and introducing the product. |
| 7. | Collecting feedback | By 30th July 2017 | To analyze the response of customers. |
Bibliography
AEMC. (2016). 2016 Retail Competition Review. Sydney: Australian Energy Market Commission.
Ball, A. (2015). Australian Energy Update. CANBERRA: Energy Program: Office of the Chief Economist.
CHURCHOUSE, N. (2009, November 10). Powershop is shown to be the cheapest. Stuff.
FREAR, G. (2014, July 1). Powershop and Nike shine on the innovation stage, here’s why. IDEA LOG. Retrieved from http://idealog.co.nz/venture/2013/07/powershop-nike-shine-innovation-stage
Gibson, J. (2013, July 2). Are these the 5 most innovative power companies in Australia? one big switch? Retrieved from https://www.onebigswitch.com.au/news/2013/07/02/are-these-the-5-most-innovative-power-companies-in-australia
Gupta, A. (2013). Environment & PEST Analysis: An Approach to External. International Journal of Modern Social Sciences, 2(1), 34-43.
News: Marketing Magazine. (2005, 4 6). Retrieved from Marketing Magazine: http://www.marketingmagazine.co.uk/news/469532/Mark-Ritson-branding-Three-telltale-signs-agencys-ineptitude/?DCMP=ILC-SEARCH
Parkinson, G. (2014, February 16). Powershop Takes On Utilities With Green Energy Supermarket. GreenTech Media. Retrieved from http://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/powershop-takes-on-utilities-with-green-energy-supermarket
Parnell, J. A. (2013). Strategic Management: Theory and Practice. Sage Publications Inc.
Peng, G. C., & Nunes, M. B. (2007). Using PEST Analysis as a Tool for Refining and Focusing. 6th European Conference on Research Methodology for Business and Management Studies, 229-237.
TUTTY, J. (2013, July 14). More than 60,000 householders make One Big Switch to cut power bills with Click Energy. The Courier-Mail. Retrieved from http://www.couriermail.com.au/news/queensland/more-than-60000-householders-make-one-big-switch-to-cut-power-bills-with-click-energy/story-fnihsrf2-1226678952284
Vorrath, S. (2016, February 24). Powershop customers up 32%, but Australian renewables market still shaky: Meridian. Renew Economy. Retrieved from http://reneweconomy.com.au/2016/powershop-customers-up-32-but-australian-renewables-market-still-shaky-meridian-99523
World, I. (2016). Electricity Retailing in Australia: Market Research Report. IBI WORLD.


